Introduction
Acetatas, commonly known as acetate, plays a pivotal role in numerous chemical and industrial processes. Derived from acetic acid, acetate is a versatile compound with applications spanning from pharmaceuticals to textiles. This article delves into the intricacies of acetates, exploring their chemical composition, significance in industrial processes, environmental impact, and ongoing research and development.
Chemical Composition of Acetatas
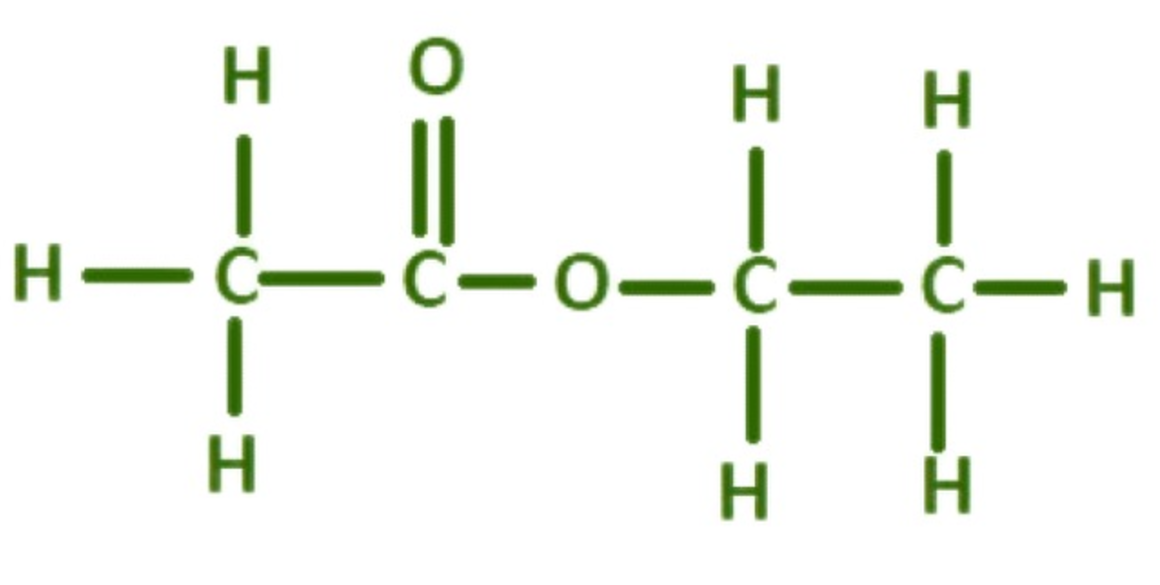
Acetates are salts or esters of acetic acid. The general formula for an acetate ion is C₂H₃O₂⁻. Acetates can combine with various cations, such as sodium (sodium acetate), potassium (potassium acetate), and calcium (calcium acetate), forming compounds with diverse properties and uses.
In chemical terms, acetic acid (CH₃COOH) loses a hydrogen ion (H⁺), leaving behind the acetate ion (CH₃COO⁻). This ion can then form salts with positively charged ions (cations) or esters with organic groups. The flexibility of acetate chemistry makes it an essential building block in many synthetic processes.
Significance in Industrial Processes
Acetates find applications across multiple industries due to their chemical stability and reactivity. Some key industrial uses include:
- Textile Industry: Acetate fibers, derived from cellulose acetate, are widely used in the production of textiles. These fibers are valued for their silk-like appearance, smooth texture, and ability to blend with other fibers, enhancing fabric quality and functionality.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sodium acetate and potassium acetate are commonly used as electrolyte replenishment agents in medical treatments. They help maintain acid-base balance in the body, making them crucial in intravenous solutions and dialysis treatments.
- Food Industry: Acetates serve as preservatives and flavoring agents. Sodium acetate, for instance, is used in snack foods to impart a tangy taste and extend shelf life.
- Chemical Synthesis: Acetates are vital intermediates in organic synthesis. Ethyl acetate, for example, is a common solvent used in the production of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, paints, and coatings.
- Photography: Historically, acetates played a significant role in photographic film production. Cellulose acetate film was a popular medium for capturing images before the advent of digital photography.
Environmental Impact of Acetatas
The production and use of acetates have both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, acetates are biodegradable, breaking down into harmless substances like water and carbon dioxide. This makes them environmentally friendly compared to many synthetic chemicals.
However, the production process of acetate compounds can have environmental drawbacks. For instance, the synthesis of cellulose acetate involves the use of acetic acid and acetic anhydride, both of which can be hazardous if not managed properly. Additionally, the production of acetic acid itself often relies on petrochemical processes, contributing to fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Efforts to mitigate these impacts include developing greener synthesis methods, such as using bio-based feedstocks for acetic acid production and improving waste management practices in acetate manufacturing.
Research and Development in Acetatas
Ongoing research aims to enhance the applications and sustainability of acetates. Key areas of focus include:
- Biodegradable Polymers: Scientists are exploring ways to produce biodegradable polymers from acetates, offering eco-friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. These polymers have potential applications in packaging, agriculture, and medical devices.
- Advanced Materials: Research is underway to develop high-performance materials from acetate compounds. For example, acetate-based nanocomposites are being investigated for their potential in electronic devices, coatings, and adhesives.
- Medical Applications: Innovations in acetate chemistry are driving advancements in drug delivery systems. Researchers are developing acetate-based carriers for targeted drug delivery, improving the efficacy and safety of treatments.
- Sustainable Production: Efforts to make acetate production more sustainable include the use of renewable resources and environmentally benign catalysts. These approaches aim to reduce the carbon footprint and environmental impact of acetate manufacturing.
Conclusion
Acetatas, or acetates, are indispensable in a myriad of industrial processes, thanks to their versatile chemical properties. From textiles and pharmaceuticals to food and photography, acetates play a crucial role in enhancing product quality and functionality. While their production and use pose environmental challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for more sustainable and innovative applications. As the world moves towards greener technologies, acetates will undoubtedly continue to be at the forefront of chemical and industrial advancements.
Read Our More Blogs:-